|
Nektar++
|
|
Nektar++
|
#include <TimeIntegrationScheme.h>
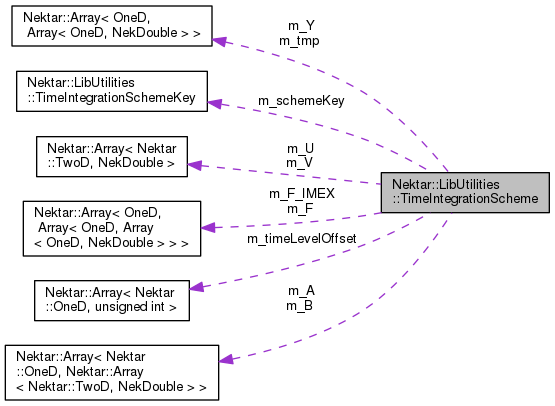
Public Types | |
| typedef const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > > | ConstTripleArray |
| typedef Array< OneD, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > > | TripleArray |
| typedef const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | ConstDoubleArray |
| typedef Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | DoubleArray |
| typedef const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > | ConstSingleArray |
| typedef Array< OneD, NekDouble > | SingleArray |
| typedef boost::function< void(ConstDoubleArray &, DoubleArray &, const NekDouble) > | FunctorType1 |
| typedef boost::function< void(ConstDoubleArray &, DoubleArray &, const NekDouble, const NekDouble) > | FunctorType2 |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual | ~TimeIntegrationScheme () |
| const TimeIntegrationSchemeKey & | GetIntegrationSchemeKey () const |
| TimeIntegrationMethod | GetIntegrationMethod () const |
| TimeIntegrationSchemeType | GetIntegrationSchemeType () const |
| NekDouble | A (const unsigned int i, const unsigned int j) const |
| NekDouble | B (const unsigned int i, const unsigned int j) const |
| NekDouble | U (const unsigned int i, const unsigned int j) const |
| NekDouble | V (const unsigned int i, const unsigned int j) const |
| NekDouble | A_IMEX (const unsigned int i, const unsigned int j) const |
| NekDouble | B_IMEX (const unsigned int i, const unsigned int j) const |
| unsigned int | GetNsteps (void) const |
| unsigned int | GetNstages (void) const |
| unsigned int | GetNmultiStepValues (void) const |
| unsigned int | GetNmultiStepDerivs (void) const |
| TimeIntegrationSolutionSharedPtr | InitializeScheme (const NekDouble timestep, ConstDoubleArray &y_0, const NekDouble time, const TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators &op) |
| This function initialises the time integration scheme. More... | |
| ConstDoubleArray & | TimeIntegrate (const NekDouble timestep, TimeIntegrationSolutionSharedPtr &y, const TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators &op) |
| Explicit integration of an ODE. More... | |
| const Array< OneD, const unsigned int > & | GetTimeLevelOffset () |
Protected Attributes | |
| TimeIntegrationSchemeKey | m_schemeKey |
| TimeIntegrationSchemeType | m_schemeType |
| unsigned int | m_numsteps |
| unsigned int | m_numstages |
| bool | m_firstStageEqualsOldSolution |
| bool | m_lastStageEqualsNewSolution |
| unsigned int | m_numMultiStepValues |
| unsigned int | m_numMultiStepDerivs |
| Array< OneD, unsigned int > | m_timeLevelOffset |
| Array< OneD, Array< TwoD, NekDouble > > | m_A |
| Array< OneD, Array< TwoD, NekDouble > > | m_B |
| Array< TwoD, NekDouble > | m_U |
| Array< TwoD, NekDouble > | m_V |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| static boost::shared_ptr< TimeIntegrationScheme > | Create (const TimeIntegrationSchemeKey &key) |
Private Attributes | |
| bool | m_initialised |
| int | m_nvar |
| bool to identify if array has been initialised More... | |
| int | m_npoints |
| The number of variables in integration scheme. More... | |
| DoubleArray | m_Y |
| The size of inner data which is stored for reuse. More... | |
| DoubleArray | m_tmp |
| Array containing the stage values. More... | |
| TripleArray | m_F |
| explicit right hand side of each stage equation More... | |
| TripleArray | m_F_IMEX |
| Array corresponding to the stage Derivatives. More... | |
| NekDouble | m_T |
| Used to store the Explicit stage derivative of IMEX schemes. More... | |
Friends | |
| template<typename > | |
| class | Nektar::MemoryManager |
| Time at the different stages. More... | |
| TimeIntegrationSchemeManagerT & | TimeIntegrationSchemeManager (void) |
Definition at line 355 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef const Array<OneD, const Array<OneD, NekDouble> > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::ConstDoubleArray |
Definition at line 361 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef const Array<OneD, const NekDouble > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::ConstSingleArray |
Definition at line 363 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef const Array<OneD, const Array<OneD, Array<OneD, NekDouble> > > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::ConstTripleArray |
Definition at line 359 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef Array<OneD, Array<OneD, NekDouble> > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::DoubleArray |
Definition at line 362 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef boost::function< void (ConstDoubleArray&, DoubleArray&, const NekDouble) > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::FunctorType1 |
Definition at line 365 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef boost::function< void (ConstDoubleArray&, DoubleArray&, const NekDouble, const NekDouble) > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::FunctorType2 |
Definition at line 366 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Definition at line 364 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
| typedef Array<OneD, Array<OneD, Array<OneD, NekDouble> > > Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::TripleArray |
Definition at line 360 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
|
inlinevirtual |
Definition at line 370 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
|
private |
Definition at line 150 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References ASSERTL1, CheckIfFirstStageEqualsOldSolution(), CheckIfLastStageEqualsNewSolution(), Nektar::LibUtilities::eAdamsBashforthOrder1, Nektar::LibUtilities::eAdamsBashforthOrder2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eAdamsBashforthOrder3, Nektar::LibUtilities::eAdamsMoultonOrder1, Nektar::LibUtilities::eAdamsMoultonOrder2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eBackwardEuler, Nektar::LibUtilities::eBDFImplicitOrder1, Nektar::LibUtilities::eBDFImplicitOrder2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eClassicalRungeKutta4, Nektar::LibUtilities::eCNAB, Nektar::LibUtilities::eDiagonallyImplicit, Nektar::LibUtilities::eDIRKOrder2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eDIRKOrder3, Nektar::LibUtilities::eExplicit, ErrorUtil::efatal, Nektar::LibUtilities::eForwardEuler, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEX, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_1_1_1, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_1_2_1, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_1_2_2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_2_2_2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_2_3_2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_2_3_3, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_3_4_3, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXdirk_4_4_3, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXGear, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXOrder1, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXOrder2, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEXOrder3, Nektar::LibUtilities::eMCNAB, Nektar::LibUtilities::eMidpoint, Nektar::LibUtilities::eRungeKutta2_ImprovedEuler, Nektar::LibUtilities::eRungeKutta2_ModifiedEuler, Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeKey::GetIntegrationMethod(), m_A, m_B, m_firstStageEqualsOldSolution, m_lastStageEqualsNewSolution, m_numMultiStepDerivs, m_numMultiStepValues, m_numstages, m_numsteps, m_schemeType, m_timeLevelOffset, m_U, m_V, NEKERROR, and VerifyIntegrationSchemeType().
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 554 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References ErrorUtil::efatal, and NEKERROR.
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 559 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References ErrorUtil::efatal, and NEKERROR.
|
inline |
Definition at line 389 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_A.
Referenced by CheckIfFirstStageEqualsOldSolution(), CheckIfLastStageEqualsNewSolution(), Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), TimeIntegrate(), and VerifyIntegrationSchemeType().
|
inline |
Definition at line 409 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_A.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), and TimeIntegrate().
|
inline |
Definition at line 394 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_B.
Referenced by CheckIfLastStageEqualsNewSolution(), Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), TimeIntegrate(), and VerifyIntegrationSchemeType().
|
inline |
Definition at line 414 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_B.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), and TimeIntegrate().
|
private |
Definition at line 1679 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References A(), Nektar::NekConstants::kNekZeroTol, m_numstages, and m_numsteps.
Referenced by TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
Definition at line 1717 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References A(), B(), Nektar::NekConstants::kNekZeroTol, m_numstages, and m_numsteps.
Referenced by TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
Definition at line 1751 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References ASSERTL1, and m_numsteps.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 143 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeManager().
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 578 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
inline |
Definition at line 379 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeKey::GetIntegrationMethod(), and m_schemeKey.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<().
|
inline |
Definition at line 374 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_schemeKey.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
inline |
Definition at line 384 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_schemeType.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), and TimeIntegrate().
|
inline |
Definition at line 434 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_numMultiStepDerivs.
|
inline |
Definition at line 429 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_numMultiStepValues.
|
inline |
Definition at line 424 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_numstages.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<().
|
inline |
Definition at line 419 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_numsteps.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<().
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 583 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
inline |
Definition at line 499 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_timeLevelOffset.
| TimeIntegrationSolutionSharedPtr Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::InitializeScheme | ( | const NekDouble | timestep, |
| ConstDoubleArray & | y_0, | ||
| const NekDouble | time, | ||
| const TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators & | op | ||
| ) |
This function initialises the time integration scheme.
Given the solution at the initial time level 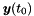 , this function generates the vectors
, this function generates the vectors ![$\boldsymbol{y}^{[n]}$](form_91.png) and
and ![$t^{[n]}$](form_92.png) needed to evaluate the time integration scheme formulated as a General Linear Method. These vectors are embedded in an object of the class TimeIntegrationSolution. This class is the abstraction of the input and output vectors of the General Linear Method.
needed to evaluate the time integration scheme formulated as a General Linear Method. These vectors are embedded in an object of the class TimeIntegrationSolution. This class is the abstraction of the input and output vectors of the General Linear Method.
For single-step methods, this function is trivial as it just wraps a TimeIntegrationSolution object around the given initial values and initial time. However, for multistep methods, actual time stepping is being done to evaluate the necessary parameters at multiple time levels needed to start the actual integration.
| timestep | The size of the timestep, i.e. 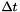 . . |
| time | on input: the initial time, i.e. 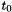 . . |
| time | on output: the new time-level after initialisation, in general this yields 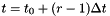 where where 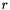 is the number of steps of the multi-step method. is the number of steps of the multi-step method. |
| nsteps | on output: he number of initialisation steps required. In general this corresponds to 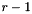 where where 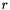 is the number of steps of the multi-step method. is the number of steps of the multi-step method. |
| f | an object of the class FuncType, where FuncType should have a method FuncType::ODEforcing to evaluate the right hand side 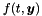 of the ODE. of the ODE. |
| y_0 | the initial value 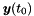 |
![$\boldsymbol{y}^{[n]}$](form_91.png) and
and ![$t^{[n]}$](form_92.png) that can be used to start the actual integration.
that can be used to start the actual integration. Definition at line 1095 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References Nektar::MemoryManager< DataType >::AllocateSharedPtr(), Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators::DoOdeRhs(), m_numMultiStepDerivs, m_numMultiStepValues, m_schemeKey, and m_timeLevelOffset.
| TimeIntegrationScheme::ConstDoubleArray & Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationScheme::TimeIntegrate | ( | const NekDouble | timestep, |
| TimeIntegrationSolutionSharedPtr & | y, | ||
| const TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators & | op | ||
| ) |
Explicit integration of an ODE.
This function explicitely perfroms a signle integration step of the ODE system:
![\[ \frac{d\boldsymbol{y}}{dt}=\boldsymbol{f}(t,\boldsymbol{y}) \]](form_99.png)
| timestep | The size of the timestep, i.e. 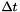 . . |
| f | an object of the class FuncType, where FuncType should have a method FuncType::ODEforcing to evaluate the right hand side 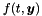 of the ODE. of the ODE. |
| y | on input: the vectors ![$\boldsymbol{y}^{[n-1]}$](form_100.png) and and ![$t^{[n-1]}$](form_101.png) (which corresponds to the solution at the old time level) (which corresponds to the solution at the old time level) |
| y | on output: the vectors ![$\boldsymbol{y}^{[n]}$](form_91.png) and and ![$t^{[n]}$](form_92.png) (which corresponds to the solution at the old new level) (which corresponds to the solution at the old new level) |
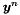 at the new time level (which in fact is also embedded in the argument y).
at the new time level (which in fact is also embedded in the argument y). Definition at line 1136 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References Nektar::MemoryManager< DataType >::AllocateSharedPtr(), ASSERTL1, Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators::DoOdeRhs(), Nektar::LibUtilities::eImplicit, GetIntegrationSchemeKey(), GetIntegrationSchemeType(), m_numMultiStepDerivs, m_numMultiStepValues, m_numsteps, m_timeLevelOffset, and Vmath::Smul().
|
private |
Definition at line 1361 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References A(), A_IMEX(), ASSERTL1, B(), B_IMEX(), CheckTimeIntegrateArguments(), Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators::DoImplicitSolve(), Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators::DoOdeRhs(), Nektar::LibUtilities::TimeIntegrationSchemeOperators::DoProjection(), Nektar::LibUtilities::eDiagonallyImplicit, Nektar::LibUtilities::eExplicit, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEX, GetFirstDim(), GetIntegrationSchemeType(), GetSecondDim(), Nektar::NekConstants::kNekZeroTol, m_F, m_F_IMEX, m_firstStageEqualsOldSolution, m_initialised, m_lastStageEqualsNewSolution, m_npoints, m_numstages, m_numsteps, m_nvar, m_T, m_tmp, m_Y, Vmath::Smul(), Vmath::Svtvp(), U(), V(), Vmath::Vcopy(), Vmath::Vsub(), and Vmath::Zero().
|
inline |
Definition at line 399 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_U.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), and TimeIntegrate().
|
inline |
Definition at line 404 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
References m_V.
Referenced by Nektar::LibUtilities::operator<<(), and TimeIntegrate().
|
private |
Definition at line 1040 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
References A(), ASSERTL1, B(), Nektar::LibUtilities::eDiagonallyImplicit, Nektar::LibUtilities::eExplicit, Nektar::LibUtilities::eIMEX, Nektar::LibUtilities::eImplicit, and Nektar::NekConstants::kNekZeroTol.
Referenced by TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
friend |
Time at the different stages.
Definition at line 546 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
|
friend |
Definition at line 45 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.cpp.
Definition at line 529 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by A(), A_IMEX(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
Definition at line 530 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by B(), B_IMEX(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
explicit right hand side of each stage equation
Definition at line 541 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
private |
Array corresponding to the stage Derivatives.
Definition at line 542 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
protected |
Definition at line 511 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
Definition at line 535 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
protected |
Definition at line 512 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
The number of variables in integration scheme.
Definition at line 537 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
protected |
Definition at line 516 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by GetNmultiStepDerivs(), InitializeScheme(), TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
protected |
Definition at line 514 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by GetNmultiStepValues(), InitializeScheme(), TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
protected |
Definition at line 509 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by CheckIfFirstStageEqualsOldSolution(), CheckIfLastStageEqualsNewSolution(), GetNstages(), TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
protected |
Definition at line 508 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by CheckIfFirstStageEqualsOldSolution(), CheckIfLastStageEqualsNewSolution(), CheckTimeIntegrateArguments(), GetNsteps(), TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
bool to identify if array has been initialised
Definition at line 536 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
|
protected |
Definition at line 506 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by GetIntegrationMethod(), GetIntegrationSchemeKey(), and InitializeScheme().
|
protected |
Definition at line 507 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by GetIntegrationSchemeType(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
Used to store the Explicit stage derivative of IMEX schemes.
Definition at line 544 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
Definition at line 518 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by GetTimeLevelOffset(), InitializeScheme(), TimeIntegrate(), and TimeIntegrationScheme().
|
private |
Array containing the stage values.
Definition at line 539 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
Definition at line 531 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrationScheme(), and U().
Definition at line 532 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrationScheme(), and V().
|
private |
The size of inner data which is stored for reuse.
Definition at line 538 of file TimeIntegrationScheme.h.
Referenced by TimeIntegrate().
 1.8.9.1
1.8.9.1