| Equation to solve |
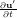 + L(U,u′) = -∇p + ν∇2u′ + L(U,u′) = -∇p + ν∇2u′ |
The type of equation which is to be solved is specified through the EqType option in the
session file. This can be set to any of the following:
| Equation to solve |
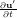 + L(U,u′) = -∇p + ν∇2u′ + L(U,u′) = -∇p + ν∇2u′ |
| Equation Type | Dimensions | Projections | Algorithms |
| UnsteadyNavierStokes | 2D, Quasi-3D | Continuous | VCS,DS |
Eqtype: sets the type of equation to solve, according to the table above.
TimeIntegrationMethod: the following types of time integration methods have been
tested with each solver:
| Explicit | Diagonally Implicit | IMEX | Implicit | |
UnsteadyNavierStokes | X | X | ||
Projection: the Galerkin projection used may be either
Continuous: for a C0-continuous Galerkin (CG) projection;
Discontinuous: for a discontinous Galerkin (DG) projection.EvolutionOperator:
Nonlinear (non-linear Navier-Stokes equations).
Direct (linearised Navier-Stokes equations).
Adjoint (adjoint Navier-Stokes equations).
TransientGrowth ((transient growth evolution operator).Driver: specifies the type of problem to be solved:
Standard (time integration of the equations)
ModifiedArnoldi (computations of the leading eigenvalues and eigenmodes
using modified Arnoldi method)
Arpack (computations of eigenvalues/eigenmodes using Implicitly Restarted
Arnoldi Method (ARPACK) ).ArpackProblemType: types of eigenvalues to be computed (for Driver Arpack
only)
LargestMag (eigenvalues with largest magnitude).
SmallestMag (eigenvalues with smallest magnitude).
LargestReal (eigenvalues with largest real part).
SmallestReal (eigenvalues with smallest real part).
LargestImag (eigenvalues with largest imaginary part).
SmallestIma (eigenvalues with smallest imaginary part ).Homogeneous: specifies the Fourier expansion in a third direction (optional)
1D (Fourier spectral method in z-direction).ModeType: this specifies the type of the quasi-3D problem to be solved.
MultipleMode (stability analysis with multiple modes).
SingleMode (BiGlobal Stability Analysis: full-complex mode).
HalfMode (BiGlobal Stability Analysis: half-complex mode u.Re v.Re w.Im
p.Re).
The following parameters can be specified in the PARAMETERS section of the session
file:
Re: sets the Reynolds number
Kinvis: sets the kinematic viscosity ν.
kdim: sets the dimension of the Krylov subspace κ. Can be used in:
ModifiedArnoldi and Arpack. Default value: 16.
evtol: sets the tolerance of the eigenvalues. Can be used in:
imagShift: provide an imaginary shift to the direct sovler eigenvalue problem by
the specified value. lttModifiedArnoldi and Arpack. Default value: 10-6.
nits: sets the maximum number of iterations. Can be used in: ModifiedArnoldi
and Arpack. Default value: 500.
LZ: sets the length in the spanswise direction Lz. Can be used in Homogeneous set
to 1D. Default value: 1.
HomModesZ: sets the number of planes in the homogeneous directions. Can be used
in Homogeneous set to 1D and ModeType set to MultipleModes.
N_slices: sets the number of temporal slices for Floquet stability analysis.
period: sets the periodicity of the base flow.
realShift: provide a real shift to the direct sovler eigenvalue problem by the
specified value.
When using the direct solver for stability analysis it is necessary to specify a Forcing function “StabilityCoupledLNS” in the form:
This is required since we need to tell the solver to use the existing field as a forcing function to the direct matrix inverse as part of the Arnoldi iteration.
NEKTAR/solvers/IncNavierStokesSolver/Tests. See for example the files
PPF_R15000_ModifiedArnoldi_Shift.tst and PPF_R15000_3D.xml noting that some
parameters are specified in the .tst files.