|
Nektar++
|
|
Nektar++
|
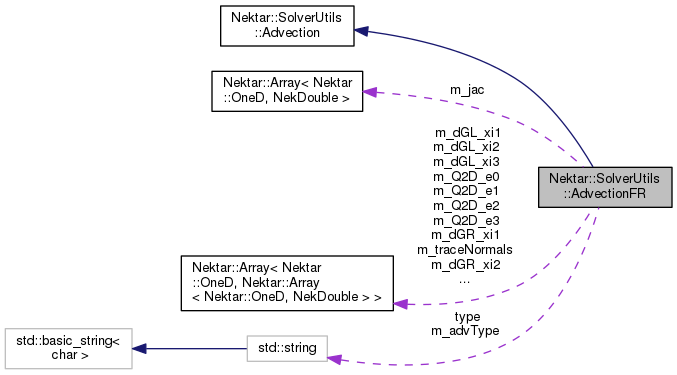
#include <AdvectionFR.h>
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static AdvectionSharedPtr | create (std::string advType) |
Public Attributes | |
| Array< OneD, NekDouble > | m_jac |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_gmat |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_Q2D_e0 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_Q2D_e1 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_Q2D_e2 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_Q2D_e3 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_dGL_xi1 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_dGR_xi1 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_dGL_xi2 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_dGR_xi2 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_dGL_xi3 |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_dGR_xi3 |
| DNekMatSharedPtr | m_Ixm |
| DNekMatSharedPtr | m_Ixp |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static std::string | type [] |
Protected Member Functions | |
| AdvectionFR (std::string advType) | |
| AdvectionFR uses the Flux Reconstruction (FR) approach to compute the advection term. The implementation is only for segments, quadrilaterals and hexahedra at the moment. More... | |
| virtual void | v_InitObject (LibUtilities::SessionReaderSharedPtr pSession, Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > pFields) |
| Initiliase AdvectionFR objects and store them before starting the time-stepping. More... | |
| virtual void | v_Advect (const int nConvectiveFields, const Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > &fields, const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &advVel, const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &inarray, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &outarray, const NekDouble &time) |
| Compute the advection term at each time-step using the Flux Reconstruction approach (FR). More... | |
| virtual void | v_SetupMetrics (LibUtilities::SessionReaderSharedPtr pSession, Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > pFields) |
| Setup the metric terms to compute the contravariant fluxes. (i.e. this special metric terms transform the fluxes at the interfaces of each element from the physical space to the standard space). More... | |
| virtual void | v_SetupCFunctions (LibUtilities::SessionReaderSharedPtr pSession, Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > pFields) |
| Setup the derivatives of the correction functions. For more details see J Sci Comput (2011) 47: 50–72. More... | |
| virtual void | v_DivCFlux_1D (const int nConvectiveFields, const Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > &fields, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX1, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &numericalFlux, Array< OneD, NekDouble > &divCFlux) |
| Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 1D problems. More... | |
| virtual void | v_DivCFlux_2D (const int nConvectiveFields, const Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > &fields, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX1, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX2, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &numericalFlux, Array< OneD, NekDouble > &divCFlux) |
| Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 2D problems. More... | |
| virtual void | v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss (const int nConvectiveFields, const Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > &fields, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX1, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX2, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &numericalFlux, Array< OneD, NekDouble > &divCFlux) |
| Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 2D problems where POINTSTYPE="GaussGaussLegendre". More... | |
| virtual void | v_DivCFlux_3D (const int nConvectiveFields, const Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > &fields, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX1, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX2, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &fluxX3, const Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &numericalFlux, Array< OneD, NekDouble > &divCFlux) |
| Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 3D problems. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection Protected Member Functions inherited from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection | |
| virtual SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT void | v_SetBaseFlow (const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &inarray) |
| Overrides the base flow used during linearised advection. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_traceNormals |
| std::string | m_advType |
 Protected Attributes inherited from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection Protected Attributes inherited from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection | |
| AdvectionFluxVecCB | m_fluxVector |
| Callback function to the flux vector (set when advection is in conservative form). More... | |
| RiemannSolverSharedPtr | m_riemann |
| Riemann solver for DG-type schemes. More... | |
| int | m_spaceDim |
| Storage for space dimension. Used for homogeneous extension. More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection Public Member Functions inherited from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT void | InitObject (LibUtilities::SessionReaderSharedPtr pSession, Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > pFields) |
| Interface function to initialise the advection object. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT void | Advect (const int nConvectiveFields, const Array< OneD, MultiRegions::ExpListSharedPtr > &fields, const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &advVel, const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &inarray, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &outarray, const NekDouble &time) |
| Interface function to advect the vector field. More... | |
| template<typename FuncPointerT , typename ObjectPointerT > | |
| void | SetFluxVector (FuncPointerT func, ObjectPointerT obj) |
| Set the flux vector callback function. More... | |
| void | SetRiemannSolver (RiemannSolverSharedPtr riemann) |
| Set a Riemann solver object for this advection object. More... | |
| void | SetFluxVector (AdvectionFluxVecCB fluxVector) |
| Set the flux vector callback function. More... | |
| void | SetBaseFlow (const Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &inarray) |
| Set the base flow used for linearised advection objects. More... | |
Definition at line 47 of file AdvectionFR.h.
|
protected |
AdvectionFR uses the Flux Reconstruction (FR) approach to compute the advection term. The implementation is only for segments, quadrilaterals and hexahedra at the moment.
Definition at line 77 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
Referenced by create().
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 50 of file AdvectionFR.h.
References AdvectionFR().
|
protectedvirtual |
Compute the advection term at each time-step using the Flux Reconstruction approach (FR).
| nConvectiveFields | Number of fields. |
| fields | Pointer to fields. |
| advVel | Advection velocities. |
| inarray | Solution at the previous time-step. |
| outarray | Advection term to be passed at the time integration class. |
Implements Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection.
Definition at line 801 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References ASSERTL0, Nektar::LibUtilities::eGaussGaussLegendre, Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection::m_fluxVector, m_gmat, m_jac, Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection::m_riemann, Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection::m_spaceDim, v_DivCFlux_1D(), v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), Vmath::Vadd(), Vmath::Vdiv(), Vmath::Vmul(), and Vmath::Vvtvvtp().
|
protectedvirtual |
Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 1D problems.
| nConvectiveFields | Number of fields. |
| fields | Pointer to fields. |
| fluxX1 | X1-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| numericalFlux | Interface flux in physical space. |
| divCFlux | Divergence of the corrective flux. |
Definition at line 1011 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References m_dGL_xi1, m_dGR_xi1, Vmath::Smul(), Vmath::Vadd(), and Vmath::Vcopy().
Referenced by v_Advect().
|
protectedvirtual |
Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 2D problems.
| nConvectiveFields | Number of fields. |
| fields | Pointer to fields. |
| fluxX1 | X1-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| fluxX2 | X2-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| numericalFlux | Interface flux in physical space. |
| divCFlux | Divergence of the corrective flux. |
Definition at line 1114 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References ASSERTL0, Nektar::StdRegions::eBackwards, m_dGL_xi1, m_dGL_xi2, m_dGR_xi1, m_dGR_xi2, m_Q2D_e0, m_Q2D_e1, m_Q2D_e2, m_Q2D_e3, m_traceNormals, Vmath::Reverse(), Vmath::Vadd(), Vmath::Vsub(), and Vmath::Vvtvvtp().
Referenced by v_Advect().
|
protectedvirtual |
Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 2D problems where POINTSTYPE="GaussGaussLegendre".
| nConvectiveFields | Number of fields. |
| fields | Pointer to fields. |
| fluxX1 | X1-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| fluxX2 | X2-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| numericalFlux | Interface flux in physical space. |
| divCFlux | Divergence of the corrective flux. |
Definition at line 1303 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References ASSERTL0, Nektar::StdRegions::eBackwards, m_dGL_xi1, m_dGL_xi2, m_dGR_xi1, m_dGR_xi2, m_Q2D_e0, m_Q2D_e1, m_Q2D_e2, m_Q2D_e3, m_traceNormals, Vmath::Neg(), Vmath::Reverse(), Vmath::Vadd(), Vmath::Vcopy(), and Vmath::Vsub().
Referenced by v_Advect().
|
protectedvirtual |
Compute the divergence of the corrective flux for 3D problems.
| nConvectiveFields | Number of fields. |
| fields | Pointer to fields. |
| fluxX1 | X1-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| fluxX2 | X2-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| fluxX3 | X3-volumetric flux in physical space. |
| numericalFlux | Interface flux in physical space. |
| divCFlux | Divergence of the corrective flux. |
Definition at line 1674 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
|
protectedvirtual |
Initiliase AdvectionFR objects and store them before starting the time-stepping.
This routine calls the virtual functions v_SetupMetrics and v_SetupCFunctions to initialise the objects needed by AdvectionFR.
| pSession | Pointer to session reader. |
| pFields | Pointer to fields. |
Reimplemented from Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection.
Definition at line 91 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References Nektar::SolverUtils::Advection::v_InitObject(), v_SetupCFunctions(), and v_SetupMetrics().
|
protectedvirtual |
Setup the derivatives of the correction functions. For more details see J Sci Comput (2011) 47: 50–72.
This routine calls 3 different bases: #eDG_DG_Left - #eDG_DG_Left which recovers a nodal DG scheme, #eDG_SD_Left - #eDG_SD_Left which recovers the SD scheme, #eDG_HU_Left - #eDG_HU_Left which recovers the Huynh scheme. The values of the derivatives of the correction function are then stored into global variables and reused into the virtual functions v_DivCFlux_1D, v_DivCFlux_2D, v_DivCFlux_3D to compute the the divergence of the correction flux for 1D, 2D or 3D problems.
| pSession | Pointer to session reader. |
| pFields | Pointer to fields. |
Definition at line 270 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References ASSERTL0, Polylib::jacobd(), m_advType, m_dGL_xi1, m_dGL_xi2, m_dGL_xi3, m_dGR_xi1, m_dGR_xi2, and m_dGR_xi3.
Referenced by v_InitObject().
|
protectedvirtual |
Setup the metric terms to compute the contravariant fluxes. (i.e. this special metric terms transform the fluxes at the interfaces of each element from the physical space to the standard space).
This routine calls the function #GetEdgeQFactors to compute and store the metric factors following an anticlockwise conventions along the edges/faces of each element. Note: for 1D problem the transformation is not needed.
| pSession | Pointer to session reader. |
| pFields | Pointer to fields. |
Definition at line 116 of file AdvectionFR.cpp.
References ASSERTL0, Nektar::SpatialDomains::eDeformed, Nektar::StdRegions::StdExpansion::GetMetricInfo(), m_gmat, m_jac, m_Q2D_e0, m_Q2D_e1, m_Q2D_e2, m_Q2D_e3, and m_traceNormals.
Referenced by v_InitObject().
|
protected |
Definition at line 79 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 65 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_1D(), v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 67 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 69 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 66 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_1D(), v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 68 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 70 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_SetupCFunctions().
Definition at line 58 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_Advect(), and v_SetupMetrics().
| DNekMatSharedPtr Nektar::SolverUtils::AdvectionFR::m_Ixm |
Definition at line 71 of file AdvectionFR.h.
| DNekMatSharedPtr Nektar::SolverUtils::AdvectionFR::m_Ixp |
Definition at line 72 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Definition at line 57 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_Advect(), and v_SetupMetrics().
Definition at line 60 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupMetrics().
Definition at line 61 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupMetrics().
Definition at line 62 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupMetrics().
Definition at line 63 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupMetrics().
Definition at line 77 of file AdvectionFR.h.
Referenced by v_DivCFlux_2D(), v_DivCFlux_2D_Gauss(), and v_SetupMetrics().
|
static |
Definition at line 55 of file AdvectionFR.h.
 1.8.8
1.8.8