|
Nektar++
|
|
Nektar++
|
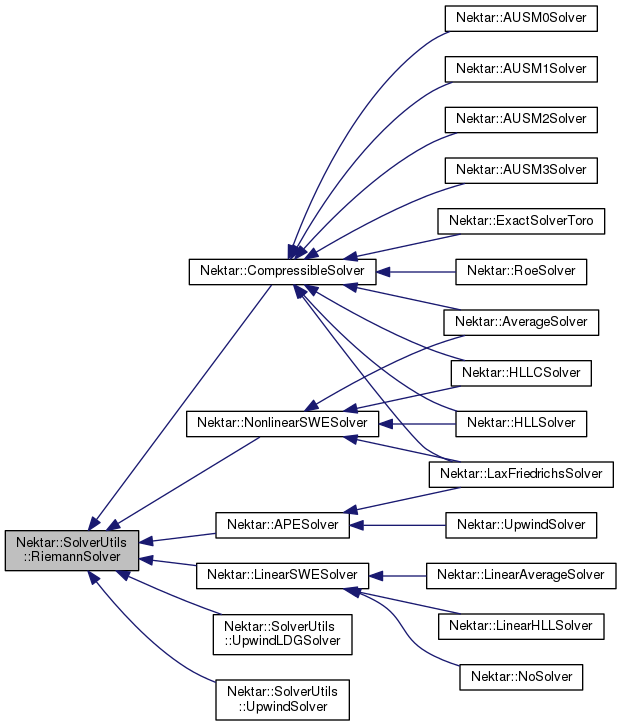
The RiemannSolver class provides an abstract interface under which solvers for various Riemann problems can be implemented. More...
#include <RiemannSolver.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT void | Solve (const int nDim, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &Fwd, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &Bwd, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &flux) |
| Perform the Riemann solve given the forwards and backwards spaces. More... | |
| template<typename FuncPointerT , typename ObjectPointerT > | |
| void | SetScalar (std::string name, FuncPointerT func, ObjectPointerT obj) |
| void | SetScalar (std::string name, RSScalarFuncType fp) |
| template<typename FuncPointerT , typename ObjectPointerT > | |
| void | SetVector (std::string name, FuncPointerT func, ObjectPointerT obj) |
| void | SetVector (std::string name, RSVecFuncType fp) |
| template<typename FuncPointerT , typename ObjectPointerT > | |
| void | SetParam (std::string name, FuncPointerT func, ObjectPointerT obj) |
| void | SetParam (std::string name, RSParamFuncType fp) |
| template<typename FuncPointerT , typename ObjectPointerT > | |
| void | SetAuxScal (std::string name, FuncPointerT func, ObjectPointerT obj) |
| template<typename FuncPointerT , typename ObjectPointerT > | |
| void | SetAuxVec (std::string name, FuncPointerT func, ObjectPointerT obj) |
| std::map< std::string, RSScalarFuncType > & | GetScalars () |
| std::map< std::string, RSVecFuncType > & | GetVectors () |
| std::map< std::string, RSParamFuncType > & | GetParams () |
Public Attributes | |
| int | m_spacedim |
Protected Member Functions | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT | RiemannSolver () |
| virtual void | v_Solve (const int nDim, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &Fwd, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &Bwd, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &flux)=0 |
| void | GenerateRotationMatrices (const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &normals) |
| Generate rotation matrices for 3D expansions. More... | |
| void | FromToRotation (Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &from, Array< OneD, const NekDouble > &to, NekDouble *mat) |
| A function for creating a rotation matrix that rotates a vector from into another vector to. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT void | rotateToNormal (const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &inarray, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &normals, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &vecLocs, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &outarray) |
| Rotate a vector field to trace normal. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT void | rotateFromNormal (const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &inarray, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &normals, const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &vecLocs, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > &outarray) |
| Rotate a vector field from trace normal. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT bool | CheckScalars (std::string name) |
| Determine whether a scalar has been defined in m_scalars. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT bool | CheckVectors (std::string name) |
| Determine whether a vector has been defined in m_vectors. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT bool | CheckParams (std::string name) |
| Determine whether a parameter has been defined in m_params. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT bool | CheckAuxScal (std::string name) |
| Determine whether a scalar has been defined in m_auxScal. More... | |
| SOLVER_UTILS_EXPORT bool | CheckAuxVec (std::string name) |
| Determine whether a vector has been defined in m_auxVec. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| bool | m_requiresRotation |
| Indicates whether the Riemann solver requires a rotation to be applied to the velocity fields. More... | |
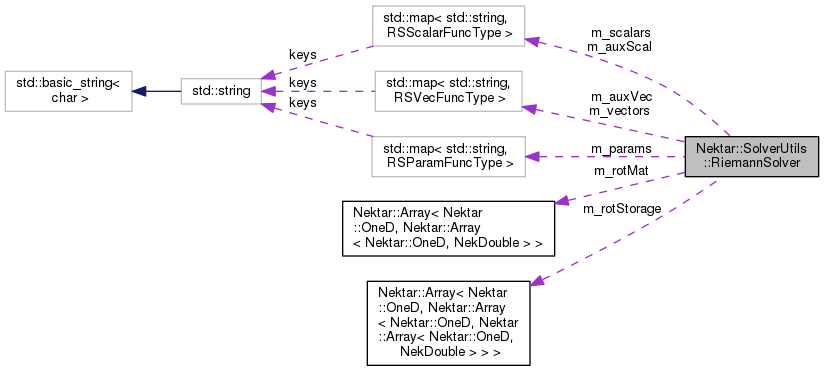
| std::map< std::string, RSScalarFuncType > | m_scalars |
| Map of scalar function types. More... | |
| std::map< std::string, RSVecFuncType > | m_vectors |
| Map of vector function types. More... | |
| std::map< std::string, RSParamFuncType > | m_params |
| Map of parameter function types. More... | |
| std::map< std::string, RSScalarFuncType > | m_auxScal |
| Map of auxiliary scalar function types. More... | |
| std::map< std::string, RSVecFuncType > | m_auxVec |
| Map of auxiliary vector function types. More... | |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > | m_rotMat |
| Rotation matrices for each trace quadrature point. More... | |
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > > | m_rotStorage |
| Rotation storage. More... | |
The RiemannSolver class provides an abstract interface under which solvers for various Riemann problems can be implemented.
Definition at line 62 of file RiemannSolver.h.
|
protected |
Definition at line 79 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
|
protected |
Determine whether a scalar has been defined in m_auxScal.
| name | Scalar name. |
Definition at line 375 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References Nektar::iterator, and m_auxScal.
|
protected |
Determine whether a vector has been defined in m_auxVec.
| name | Vector name. |
Definition at line 388 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References Nektar::iterator, and m_auxVec.
Referenced by Solve().
|
protected |
Determine whether a parameter has been defined in m_params.
| name | Parameter name. |
Definition at line 362 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References Nektar::iterator, and m_params.
Referenced by Nektar::LaxFriedrichsSolver::v_PointSolve(), and Nektar::UpwindSolver::v_PointSolve().
|
protected |
Determine whether a scalar has been defined in m_scalars.
| name | Scalar name. |
Definition at line 336 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References Nektar::iterator, and m_scalars.
Referenced by Nektar::SolverUtils::UpwindLDGSolver::v_Solve(), and Nektar::SolverUtils::UpwindSolver::v_Solve().
|
protected |
Determine whether a vector has been defined in m_vectors.
| name | Vector name. |
Definition at line 349 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References Nektar::iterator, and m_vectors.
Referenced by Nektar::APESolver::GetRotBasefield(), and Solve().
|
protected |
A function for creating a rotation matrix that rotates a vector from into another vector to.
Authors: Tomas Möller, John Hughes "Efficiently Building a Matrix to Rotate One Vector to Another" Journal of Graphics Tools, 4(4):1-4, 1999
| from | Normalised 3-vector to rotate from. |
| to | Normalised 3-vector to rotate to. |
| out | Resulting 3x3 rotation matrix (row-major order). |
Definition at line 444 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References CROSS, DOT, and EPSILON.
Referenced by GenerateRotationMatrices().
|
protected |
Generate rotation matrices for 3D expansions.
Definition at line 399 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References FromToRotation(), and m_rotMat.
Referenced by rotateToNormal().
|
inline |
Definition at line 136 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_params.
|
inline |
Definition at line 126 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_scalars.
|
inline |
Definition at line 131 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_vectors.
|
protected |
Rotate a vector field from trace normal.
This function performs a rotation of the triad of vector components provided in inarray so that the first component aligns with the Cartesian components; it performs the inverse operation of RiemannSolver::rotateToNormal.
Definition at line 255 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References ASSERTL1, m_rotMat, Vmath::Vcopy(), Vmath::Vmul(), Vmath::Vvtvm(), Vmath::Vvtvp(), and Vmath::Vvtvvtp().
Referenced by Solve().
|
protected |
Rotate a vector field to trace normal.
This function performs a rotation of a vector so that the first component aligns with the trace normal direction.
The vectors components are stored in inarray. Their locations must be specified in the "vecLocs" array. vecLocs[0] contains the locations of the first vectors components, vecLocs[1] those of the second and so on.
In 2D, this is accomplished through the transform:
![\[ (u_x, u_y) = (n_x u_x + n_y u_y, -n_x v_x + n_y v_y) \]](form_461.png)
In 3D, we generate a (non-unique) transformation using RiemannSolver::fromToRotation.
Definition at line 164 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References ASSERTL1, GenerateRotationMatrices(), m_rotMat, Vmath::Vcopy(), Vmath::Vmul(), Vmath::Vvtvm(), Vmath::Vvtvp(), and Vmath::Vvtvvtp().
Referenced by Nektar::APESolver::GetRotBasefield(), and Solve().
|
inline |
Definition at line 111 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_auxScal.
|
inline |
Definition at line 119 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_auxVec.
|
inline |
Definition at line 98 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_params.
|
inline |
Definition at line 105 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_params.
|
inline |
Definition at line 72 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_scalars.
|
inline |
Definition at line 79 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_scalars.
|
inline |
Definition at line 85 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_vectors.
|
inline |
Definition at line 92 of file RiemannSolver.h.
References m_vectors.
| void Nektar::SolverUtils::RiemannSolver::Solve | ( | const int | nDim, |
| const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > & | Fwd, | ||
| const Array< OneD, const Array< OneD, NekDouble > > & | Bwd, | ||
| Array< OneD, Array< OneD, NekDouble > > & | flux | ||
| ) |
Perform the Riemann solve given the forwards and backwards spaces.
This routine calls the virtual function v_Solve to perform the Riemann solve. If the flag m_requiresRotation is set, then the velocity field is rotated to the normal direction to perform dimensional splitting, and the resulting fluxes are rotated back to the Cartesian directions before being returned. For the Rotation to work, the normal vectors "N" and the location of the vector components in Fwd "vecLocs"must be set via the SetAuxVec() method.
| Fwd | Forwards trace space. |
| Bwd | Backwards trace space. |
| flux | Resultant flux along trace space. |
Definition at line 101 of file RiemannSolver.cpp.
References ASSERTL1, CheckAuxVec(), CheckVectors(), m_auxVec, m_requiresRotation, m_rotStorage, m_vectors, rotateFromNormal(), rotateToNormal(), and v_Solve().
|
protectedpure virtual |
Implemented in Nektar::SolverUtils::UpwindLDGSolver, Nektar::SolverUtils::UpwindSolver, Nektar::APESolver, Nektar::CompressibleSolver, Nektar::LinearSWESolver, and Nektar::NonlinearSWESolver.
Referenced by Solve().
|
protected |
Map of auxiliary scalar function types.
Definition at line 154 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by CheckAuxScal(), and SetAuxScal().
|
protected |
Map of auxiliary vector function types.
Definition at line 156 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by CheckAuxVec(), SetAuxVec(), and Solve().
|
protected |
Map of parameter function types.
Definition at line 152 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by CheckParams(), GetParams(), SetParam(), Nektar::AverageSolver::v_ArraySolve(), Nektar::HLLCSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::ExactSolverToro::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::AUSM2Solver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::AUSM0Solver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::AUSM3Solver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::AUSM1Solver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::HLLSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::LinearHLLSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::RoeSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::LinearAverageSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::AverageSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::UpwindSolver::v_PointSolve(), Nektar::LaxFriedrichsSolver::v_PointSolve(), and Nektar::HLLCSolver::v_PointSolveVisc().
|
protected |
Indicates whether the Riemann solver requires a rotation to be applied to the velocity fields.
Definition at line 146 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by Nektar::APESolver::APESolver(), Nektar::CompressibleSolver::CompressibleSolver(), Nektar::LinearSWESolver::LinearSWESolver(), Nektar::NonlinearSWESolver::NonlinearSWESolver(), and Solve().
Rotation matrices for each trace quadrature point.
Definition at line 158 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by GenerateRotationMatrices(), rotateFromNormal(), and rotateToNormal().
|
protected |
Map of scalar function types.
Definition at line 148 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by CheckScalars(), GetScalars(), SetScalar(), Nektar::LinearSWESolver::v_Solve(), Nektar::SolverUtils::UpwindLDGSolver::v_Solve(), and Nektar::SolverUtils::UpwindSolver::v_Solve().
| int Nektar::SolverUtils::RiemannSolver::m_spacedim |
Definition at line 141 of file RiemannSolver.h.
|
protected |
Map of vector function types.
Definition at line 150 of file RiemannSolver.h.
Referenced by CheckVectors(), Nektar::APESolver::GetRotBasefield(), GetVectors(), SetVector(), and Solve().
 1.8.8
1.8.8