15.4 Flow Chart of CompressibleFlowSolver
The main procedures for building a solver are briefly introduced using the explicit solver of the
NS equations as an example. Besides the main solver class ( CompressibleFlowSolver) which
controls the solving procedure, an equation system class is needed. The equation system
classes ( EulerCFE or NavierStokesCFE) are instantiated and initialized dynamically based
on user inputs using a factory method pattern [?], which is also extensively used for the
dynamic object creation of classes in the solver. The equation system class inherits
instantiations of classes related to geometry information, solution approximation,
time integration and others from equations system classes in the libraries such as
UnsteadySystem in SolverUtils. Thus the main functionality of the equation system
class is to offer equation system related functions and to form spatial discretization
operators using numerical methods from the libraries such as, AdvectionWeakDG.
Fig. 15.2 illustrates the class structure of the explicit and implicit solvers. The equation
of state ( EquationOfState), boundary conditions ( CFSBndCond), Riemann flux
( RiemmanSolver), shock capturing method ( ArtificialDiffusion), forcing term
( Forcing), advection flux (function pointer F) and diffusion flux (function pointer G) are
instantiated or implemented in the equation system class. Specific numerical schemes like
the weak DG scheme for advection terms ( AdvectionWeakDG) and the interior
penalty method for diffusion terms ( DiffusionIP) are instantiated to calculate ∇⋅F
and ∇⋅G in Eq. (15.1) provided with all these equation system related functions
( F and G). Finally the spatial discretization operator Lδ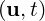 is linked to the
time integration class using the pointer-to-function
is linked to the
time integration class using the pointer-to-function A and the explicit solver is
complete.
The main simulation flowchart of the implicit solver is given in Tab. 15.2, which also shows the
flow between different classes.
Table 15.2 Nassi–Shneiderman diagram of the implicit solver with the corresponding class
names. Brown: library class ; cyan: solver class.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Initialization
in CompressibleFlowSolver
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Time step loop n
in UnsteadySystem
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | Runge-Kutta loop m = 1,  ,M | in TimeIntegrationScheme
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | Calculate source term S
m | in TimeIntegrationScheme
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | Netwon iteration l |
in NewtonSolver |
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | Calculate residual N 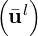 | in CFSImplicit
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | GMRES iteration k | in NekLinSysIterGMRES
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | Calculate search vector qk | in NekLinSysIterGMRES
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | BRJ iteration j = 1,  ,J | in PrecondBRJ
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | | | in CFSImplicit
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | Calculate ∂N∕∂u ⋅ 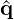 J J | in CFSImplicit
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | Calculate linear system residual | in NekLinSysIterGMRES
|
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | Calculate ul+1 by linear combination of qk | in NekLinSysIterGMRES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | Calculate un+1 | in TimeIntegrationScheme
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Output and finalization
in CompressibleFlowSolver
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |

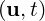 is linked to the
time integration class using the pointer-to-function
is linked to the
time integration class using the pointer-to-function  ,M
,M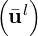
 ,J
,J 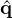 j =
j = 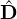 -1
-1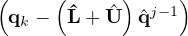
 J
J