|
Nektar++
|
|
Nektar++
|
#include <ProcessSpherigon.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ProcessSpherigon (MeshSharedPtr m) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| virtual | ~ProcessSpherigon () |
| Destructor. | |
| virtual void | Process () |
| Write mesh to output file. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Nektar::Utilities::ProcessModule Public Member Functions inherited from Nektar::Utilities::ProcessModule | |
| ProcessModule (FieldSharedPtr p_f) | |
| ProcessModule (MeshSharedPtr p_m) | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Nektar::Utilities::Module Public Member Functions inherited from Nektar::Utilities::Module | |
| Module (FieldSharedPtr p_f) | |
| virtual void | Process (po::variables_map &vm)=0 |
| void | RegisterConfig (string key, string value) |
| Register a configuration option with a module. | |
| void | PrintConfig () |
| Print out all configuration options for a module. | |
| void | SetDefaults () |
| Sets default configuration options for those which have not been set. | |
| bool | GetRequireEquiSpaced (void) |
| void | SetRequireEquiSpaced (bool pVal) |
| Module (MeshSharedPtr p_m) | |
| void | RegisterConfig (string key, string value) |
| void | PrintConfig () |
| void | SetDefaults () |
| MeshSharedPtr | GetMesh () |
| virtual void | ProcessVertices () |
| Extract element vertices. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static boost::shared_ptr< Module > | create (MeshSharedPtr m) |
| Creates an instance of this class. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static ModuleKey | className |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | GenerateNormals (vector< ElementSharedPtr > &el, MeshSharedPtr &mesh) |
| Generate a set of approximate vertex normals to a surface represented by line segments in 2D and a hybrid triangular/quadrilateral mesh in 3D. | |
| double | CrossProdMag (Node &a, Node &b) |
Calculate the magnitude of the cross product 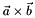 . . | |
| void | UnitCrossProd (Node &a, Node &b, Node &c) |
| double | Blend (double r) |
Calculate the  blending function for spherigon implementation. blending function for spherigon implementation. | |
| void | SuperBlend (vector< double > &r, vector< Node > &Q, Node &P, vector< double > &blend) |
Calculate the 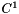 blending function for spherigon implementation. blending function for spherigon implementation. | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from Nektar::Utilities::Module Protected Attributes inherited from Nektar::Utilities::Module | |
| FieldSharedPtr | m_f |
| Field object. | |
| map< string, ConfigOption > | m_config |
| List of configuration values. | |
| bool | m_requireEquiSpaced |
| MeshSharedPtr | m_mesh |
| Mesh object. | |
This class implements the spherigon surface smoothing technique which is documented in
"The SPHERIGON: A Simple Polygon Patch for Smoothing Quickly your Polygonal Meshes": P. Volino and N. Magnenat Thalmann, Computer Animation Proceedings (1998).
This implementation works in both a 2D manifold setting (for triangles and quadrilaterals embedded in 3-space) and in a full 3D enviroment (prisms, tetrahedra and hexahedra).
No additional information needs to be supplied directly to the module in order for it to work. However, 3D elements do rely on the mapping Mesh::spherigonSurfs to be populated by the relevant input modules.
Additionally, since the algorithm assumes normals are supplied which are perpendicular to the true surface defined at each vertex. If these are specified in Mesh::vertexNormals by the input module, better smoothing results can be obtained. Otherwise, normals are estimated by taking the average of all edge/face normals which connect to the vertex.
Definition at line 47 of file ProcessSpherigon.h.
| Nektar::Utilities::ProcessSpherigon::ProcessSpherigon | ( | MeshSharedPtr | m | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 90 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
References Nektar::Utilities::Module::m_config.
|
virtual |
|
protected |
Calculate the  blending function for spherigon implementation.
blending function for spherigon implementation.
See equation (5) of the paper.
| r | Barycentric coordinate. |
Definition at line 153 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
|
inlinestatic |
Creates an instance of this class.
Definition at line 51 of file ProcessSpherigon.h.
Calculate the magnitude of the cross product 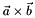 .
.
Definition at line 137 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
References Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_x, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_y, and Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_z.
Referenced by Process().
|
protected |
Generate a set of approximate vertex normals to a surface represented by line segments in 2D and a hybrid triangular/quadrilateral mesh in 3D.
This routine approximates the true vertex normals to a surface by averaging the normals of all edges/faces which connect to the vertex. It is better to use the exact surface normals which can be set in Mesh::vertexNormals, but where they are not supplied this routine calculates an approximation for the spherigon implementation.
| el | Vector of elements denoting the surface mesh. |
Definition at line 223 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
References Nektar::Utilities::Node::abs2(), ASSERTL0, Nektar::LibUtilities::eQuadrilateral, Nektar::LibUtilities::eSegment, Nektar::LibUtilities::eTriangle, Nektar::iterator, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_x, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_y, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_z, and UnitCrossProd().
Referenced by Process().
|
virtual |
Write mesh to output file.
Perform the spherigon smoothing technique on the mesh.
Implements Nektar::Utilities::Module.
Definition at line 297 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
References Nektar::Utilities::Node::abs2(), ASSERTL0, ASSERTL1, CrossProdMag(), Nektar::Utilities::Node::dot(), Nektar::LibUtilities::eGaussLobattoLegendre, Nektar::LibUtilities::eGaussRadauMAlpha1Beta0, Nektar::LibUtilities::eModified_A, Nektar::LibUtilities::eNodalTriElec, Nektar::LibUtilities::eOrtho_A, Nektar::LibUtilities::eOrtho_B, Nektar::LibUtilities::eQuadrilateral, Nektar::LibUtilities::eSegment, Nektar::LibUtilities::eTriangle, GenerateNormals(), Nektar::ParseUtils::GenerateSeqVector(), Nektar::ParseUtils::GenerateUnOrderedVector(), GetEdge(), Nektar::Utilities::GetElementFactory(), Nektar::iterator, Nektar::Utilities::Module::m_config, Nektar::Utilities::Module::m_mesh, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_x, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_y, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_z, SuperBlend(), and Vmath::Zero().
|
protected |
Calculate the 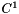 blending function for spherigon implementation.
blending function for spherigon implementation.
See equation (10) of the paper.
| r | Generalised barycentric coordinates of the point P. |
| Q | Vector of vertices denoting this triangle/quad. |
| P | Point in the triangle to apply blending to. |
| blend | The resulting blending components for each vertex. |
Definition at line 169 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
References TOL_BLEND.
Referenced by Process().
Definition at line 118 of file ProcessSpherigon.cpp.
References Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_x, Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_y, and Nektar::Utilities::Node::m_z.
Referenced by GenerateNormals().
|
static |
Definition at line 55 of file ProcessSpherigon.h.
 1.8.1.2
1.8.1.2